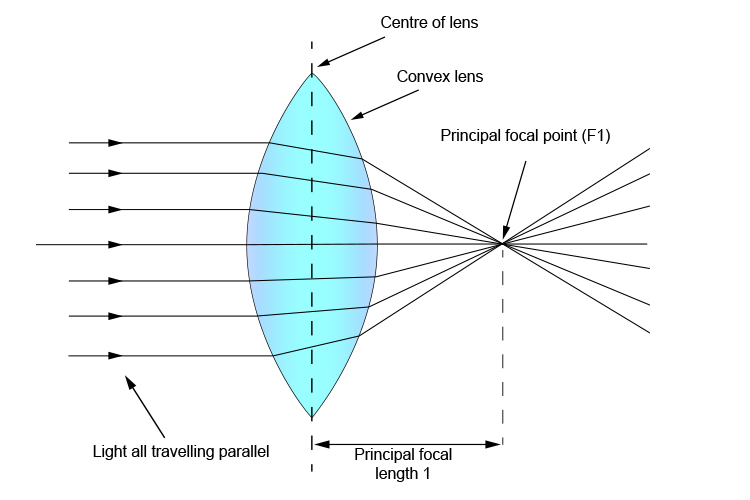
Principal focal length
Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror. The image in a plane mirror has the same size as the object, is upright, and is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.. (i.e., a virtual focus). Principal ray 2 travels first on the line going through.
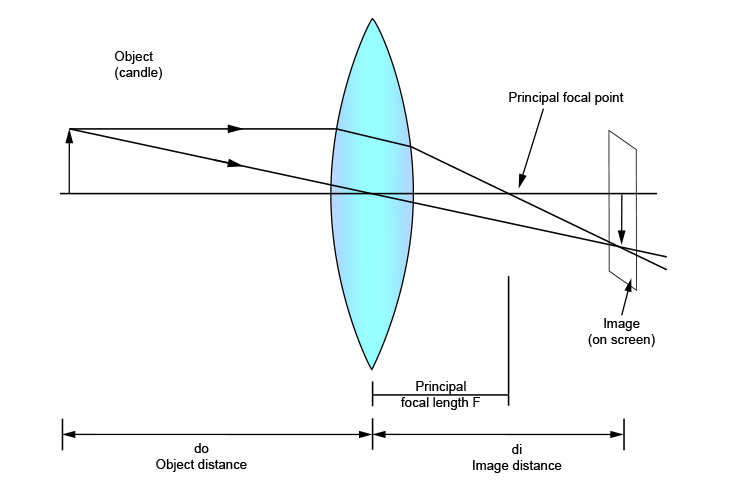
Practical ways ways to find the principal focal length len
1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis.

[DIAGRAM] Practice Drawing Ray Diagrams
Use ray diagrams and the mirror equation to calculate the properties of an image in a spherical mirror.. Principal ray 2 travels first on the line going through the focal point and then is reflected back along a line parallel to the optical axis. Principal ray 3 travels toward the center of curvature of the mirror, so it strikes the mirror.
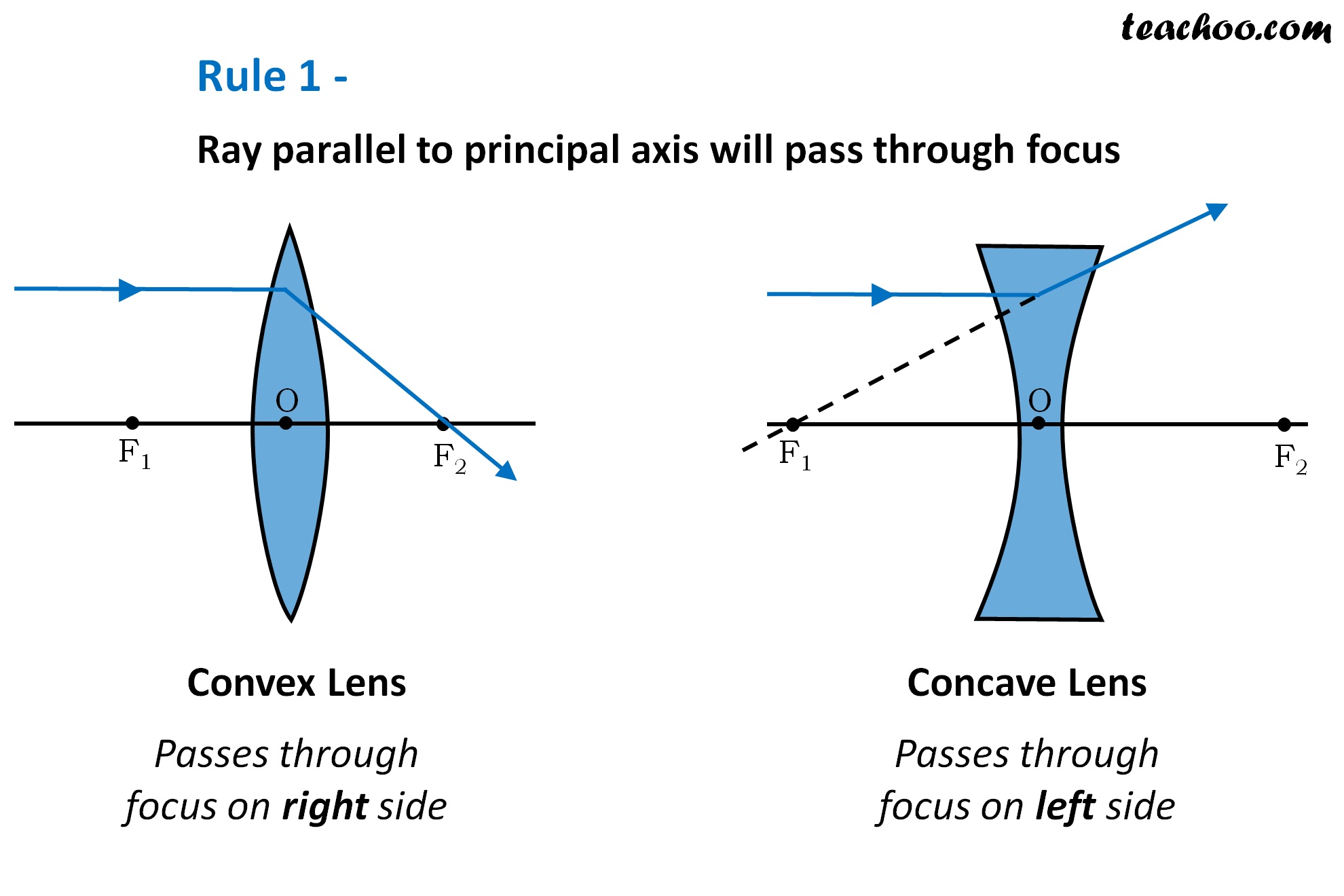
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
A completed ray diagram is shown in; The angle in which a light ray hits the mirror is the same angle in which it will be reflected back. If, for example, a light ray leaves the top of an object travelling parallel to the principal axis, it will hit the mirror at a 0 degree angle, and be reflected back at 0 degrees.

Convex Mirror Ray diagram, Images Formed with Steps Teachoo
1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the mirror. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis.

Convex lens principal rays YouTube
A ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen.. The bottom of the object will sit on the principal axis, and the top of the object will sit above the principal axis. The object will be drawn as an arrow in order to make.

Diverging lens principal rays YouTube
Describe and predict image formation and magnification as a consequence of refraction through convex and concave lenses, use ray diagrams to confirm image formation, and discuss how these properties of lenses determine their applications Explain how the human eye works in terms of geometric optics

Principal ray pattern in InI together with the firstorder sampling... Download Scientific Diagram
A ray diagram is a tool that is used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a mirror. Ray diagrams for concave mirrors were drawn in Lesson 3. In this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for convex mirrors. Step-by-Step Procedure for Drawing Ray Diagrams
Convex Mirror and Concave Mirrors Ray Diagrams, Formulae 2023
Ray Diagrams. All lenses and mirrors can use ray diagrams to find images. There are three principal rays. The first principal ray occurs when the light comes in parallel to the principle axis, it goes out through the focus. The second principal ray occurs when light comes in through the focus, then it comes out parallel to the principle axis.

Draw ray diagram to show the principal focus of a Tutorix
Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. Draw a ray which passes from the object through the centre of the lens. Some ray diagrams may also show a third ray.
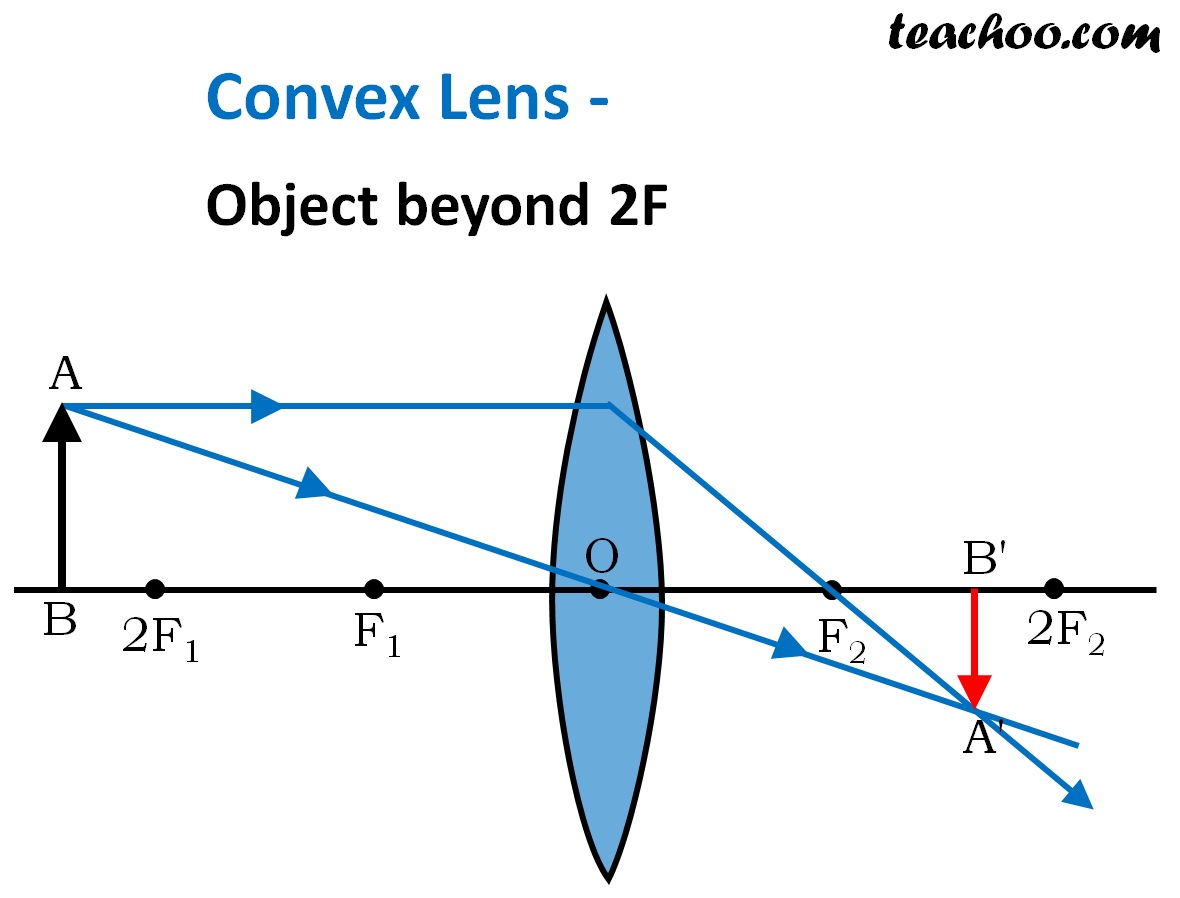
Convex Lens Ray diagram, Image Formation, Table Teachoo
Ray Diagrams Light is one of the cornerstones of physics. By understanding how light behaves, we have been able to create tools that change the way it travels. Some examples include mirrors and lenses, which we combine to make telescopes for studying distant stars or microscopes to observe life at the microscopic level.
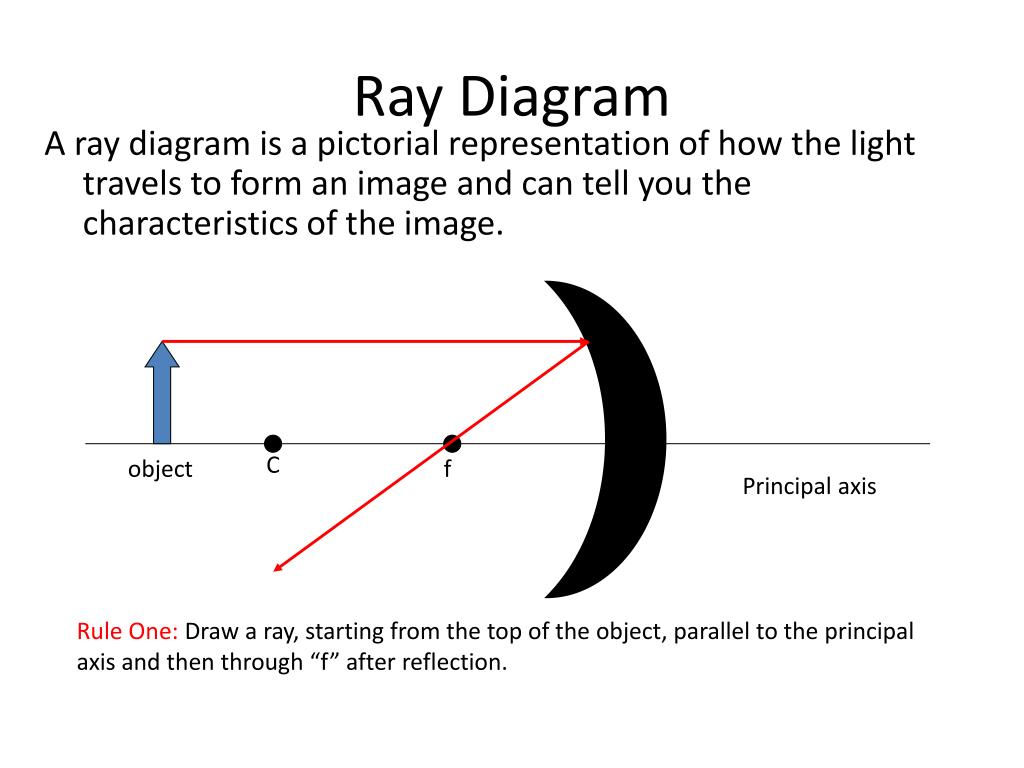
PPT Chapter 26 Geometrical Optics PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID438780
Diagram of rays at a surface, where is the angle of incidence, is the angle of reflection, and is the angle of refraction. An incident ray is a ray of light that strikes a surface. The angle between this ray and the perpendicular or normal to the surface is the angle of incidence.

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a lens. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were drawn in a previous part of Lesson 5. In this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for double concave lenses. Step-by-Step Method for Drawing Ray Diagrams
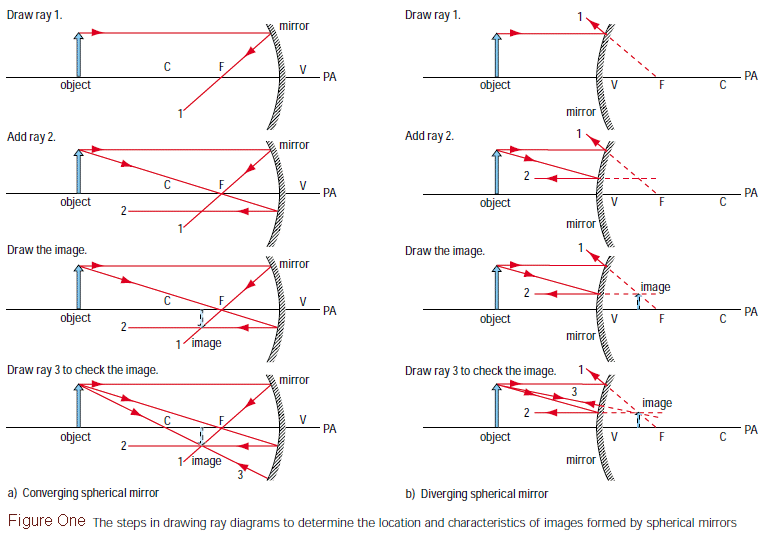
Principal Ray Diagram Diverging Lens
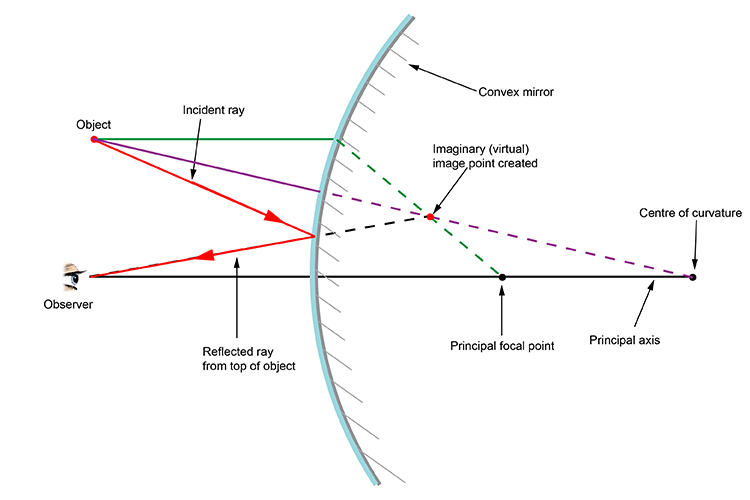
Convex mirror has two ray diagrams because its principal focus and the centre of curvature lies behind its reflecting surface. Therefore, not more than two positions of the object can be obtained in relation to these points unlike concave mirrors where more than two ray diagrams are constructed to find out the position of the image for different relative positions of the object.
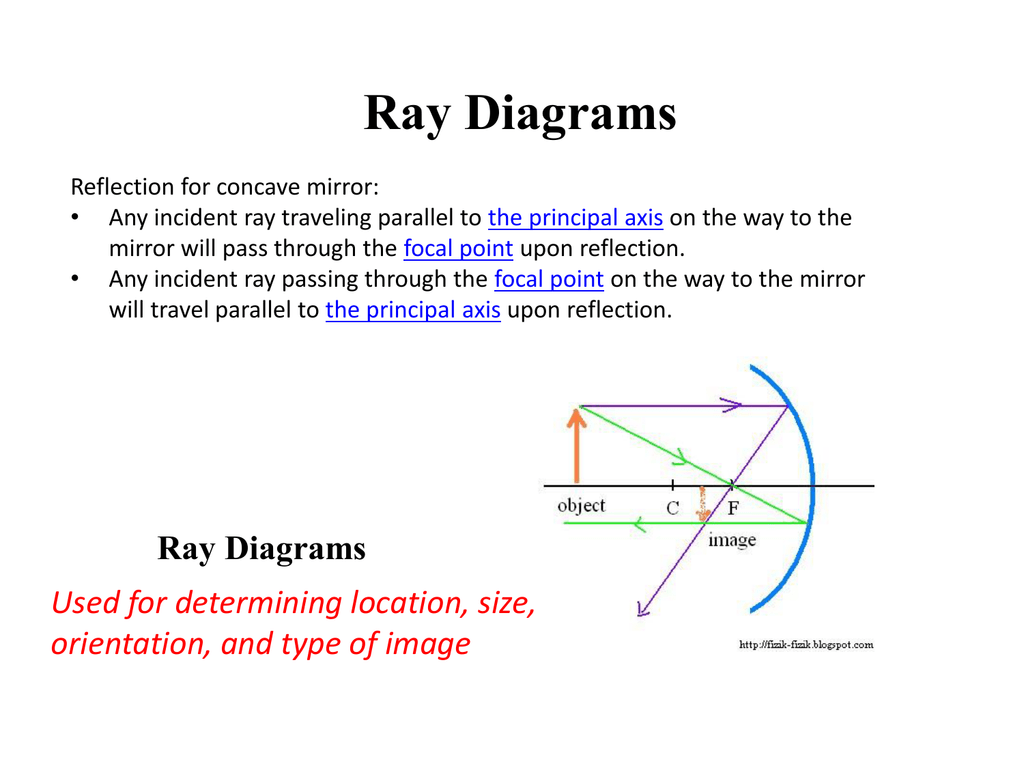
Ray Diagrams
Previously in Lesson 5, ray diagrams were constructed in order to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by double concave lenses (i.e., diverging lenses). The ray diagram constructed earlier for a diverging lens revealed that the image of the object was virtual, upright, reduced in size and located on the same side of the lens as the object.

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: