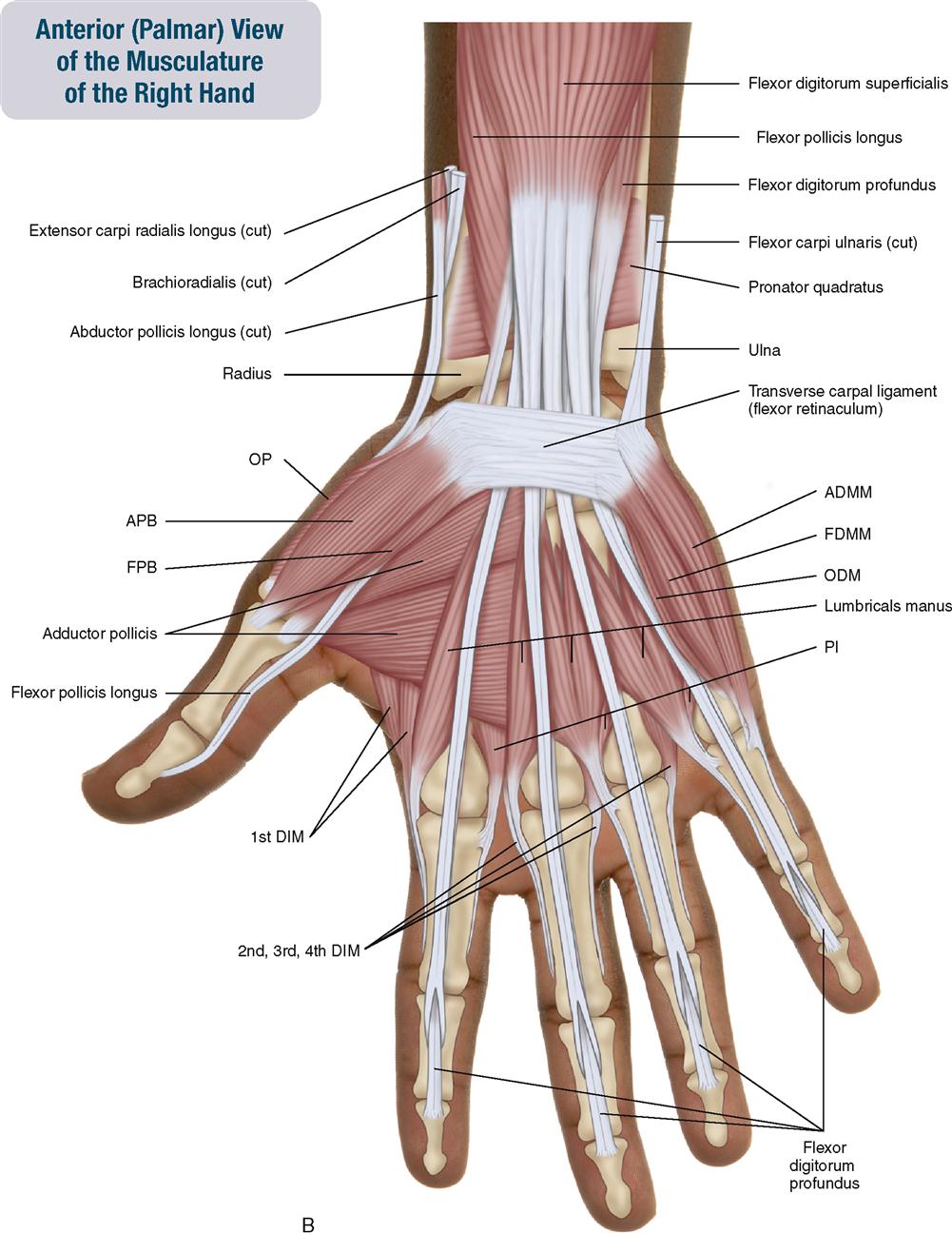
7. Muscles of the Forearm and Hand Musculoskeletal Key
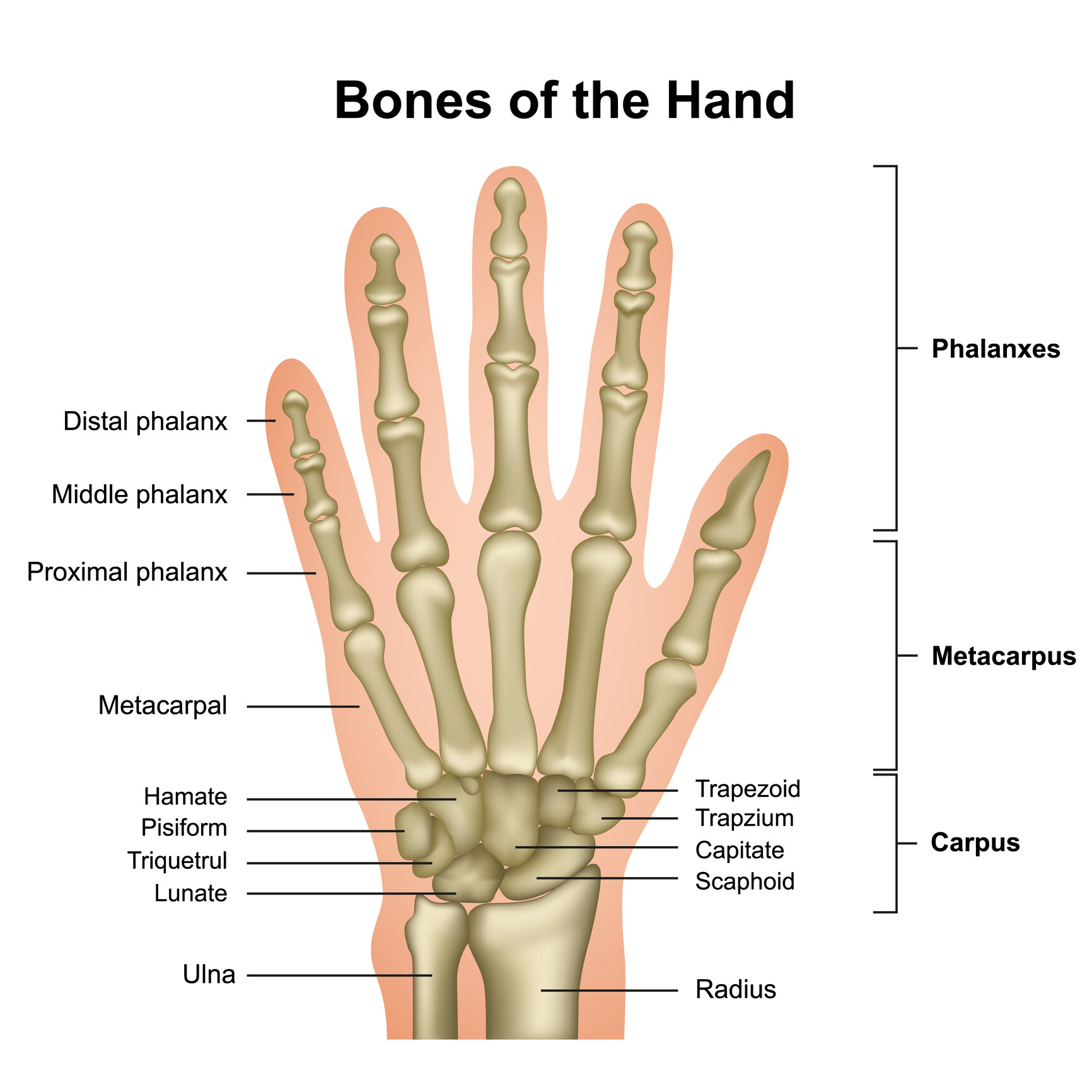
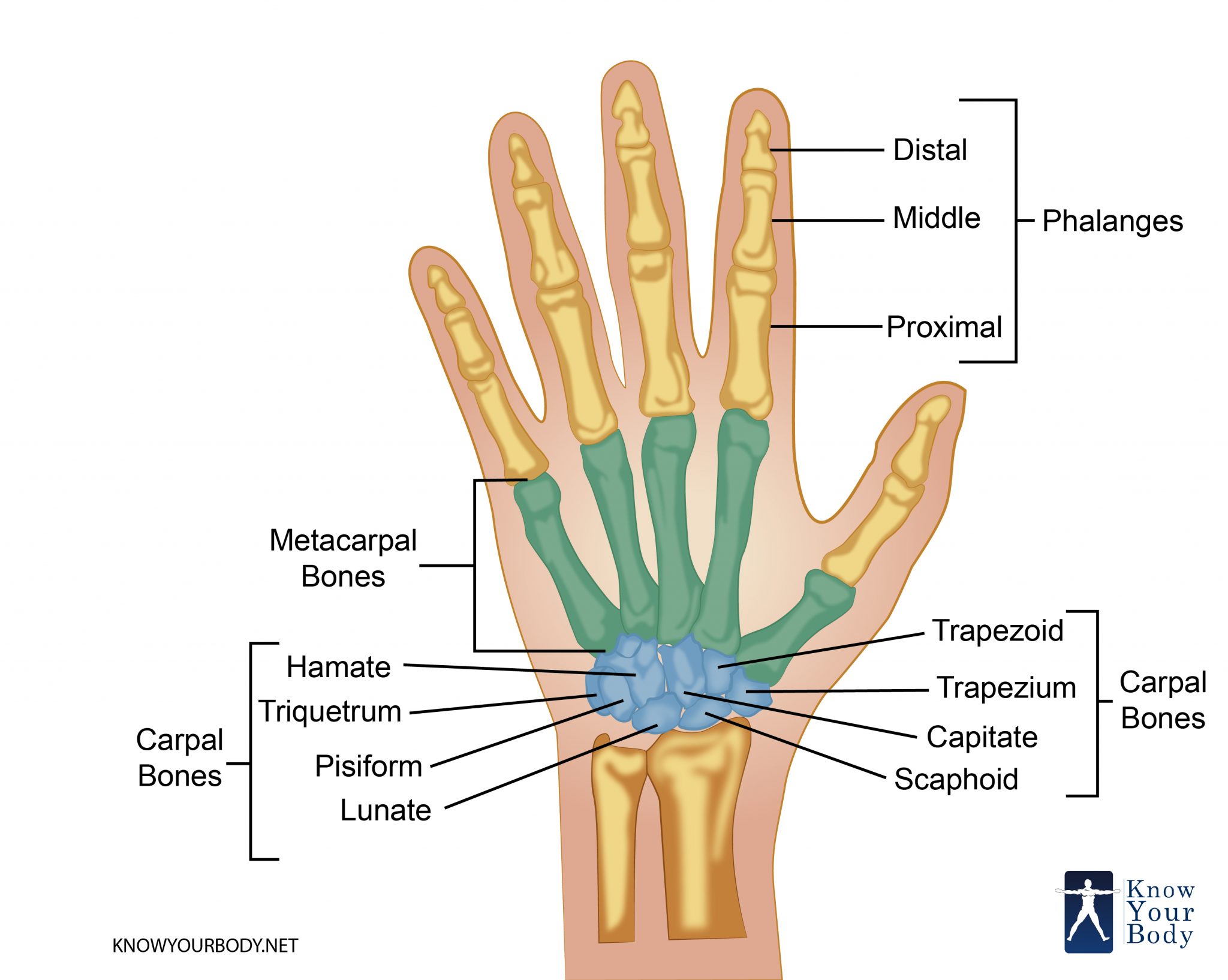
Capitate: The largest of the wrist bones, this rests between the trapezoid and the hamate behind the middle and ring fingers. Hamate: This small bone has a hook on the palmar side. It rests next.
Joint Replacements for the Hand JOI Jacksonville Orthopaedic Institute
The hand has 27 bones: the 8 bones of the carpus (wrist), arranged in two sets of four; the 5 bones of the metacarpus, one to each digit; and the 14 digital bones, or phalanges, 2 in the thumb and 3 in each finger. The carpal bones fit into a shallow socket formed by the bones of the forearm.
Hand Anatomy Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
The human hand has 27 bones: the carpals or wrist accounts for 8; the metacarpals or palm contains five; the remaining fourteen are digital bones; fingers and thumb. The palm has five bones known as metacarpal bones, one to each of the 5 digits. These metacarpals have a head, a shaft, and a base.

Hands and Musculoskeletal Conditions MSK Australia
The hand is made up of many bones: 5 elongated metacarpal bones, which are next to the wrist and help to make up the palm; 14 phalanges which make up the fingers. Each finger is made up of 3 phalanges; the thumb is made up of 2. These 19 bones collectively form 14 separate joints.
Hand Bones Anatomy, Structure and Diagram
To understand the anatomy of the hand we first must understand the anatomy of the forearm and wrist. The forearm consists of two bones, the radius and the ulna. Both forearm bones articulate with the carpal bones of the wrist distally. The radius articulates with the cashew shaped scaphoid bone, and the croissant or moon-shaped lunate bone.

Anatomy Of Hand Ligaments ANATOMY
Fig 1 - Overview of the bones of the hand. Carpal Bones The carpal bones are a group of eight, irregularly shaped bones. They are organised into two rows: proximal and distal. Collectively, the carpal bones form an arch in the coronal plane.

hand Definition, Anatomy, Bones, Diagram, & Facts Britannica
Anatomy Where are the hand and wrist located? Your wrist is the joint at the end of your forearm. It's the hinge between your arm and hand that lets you reposition your hand. Your hand begins where your wrist ends. It includes your palm, fingers and thumb. Advertisement How are the hand and wrist structured?
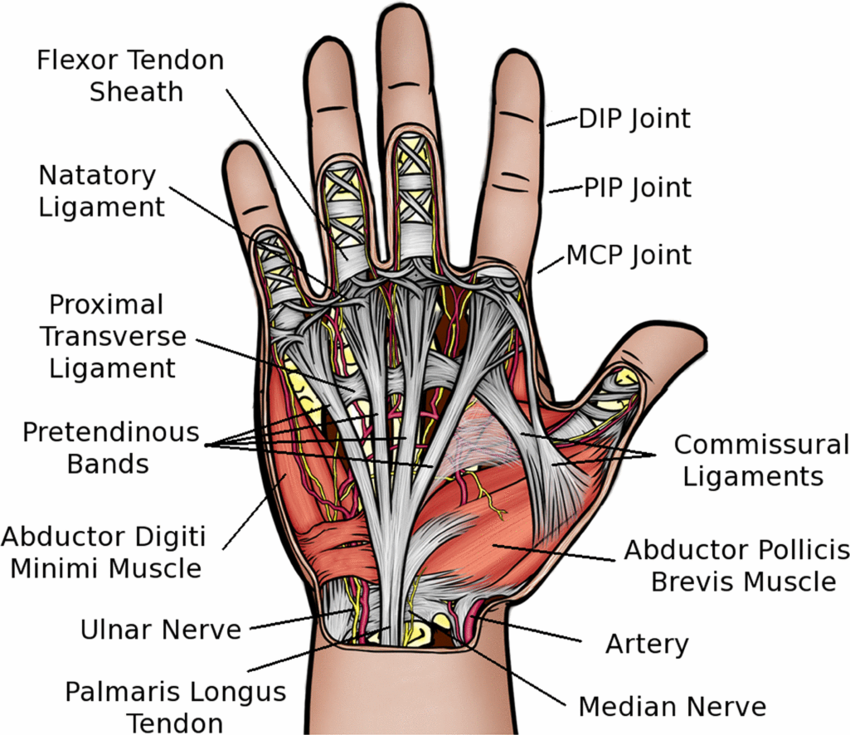
Hand Image Back in Action
The bones of the hand can be divided into three distinct groups: Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Each group of hand bones is important in its own right, but the eight carpals are especially interesting because they are arranged in two distinct rows and are direct contributors to the formation of the wrist. We'll come back to the wrist later on.

Hand and Wrist Anatomical Chart Canada Clinic Supply
Anatomy of the Hand Hand and Arm Surgery Orthopedics Anatomy of the Hand The hand is composed of many different bones, muscles, and ligaments that allow for a large amount of movement and dexterity. There are 3 major types of bones in the hand itself, including: Phalanges.
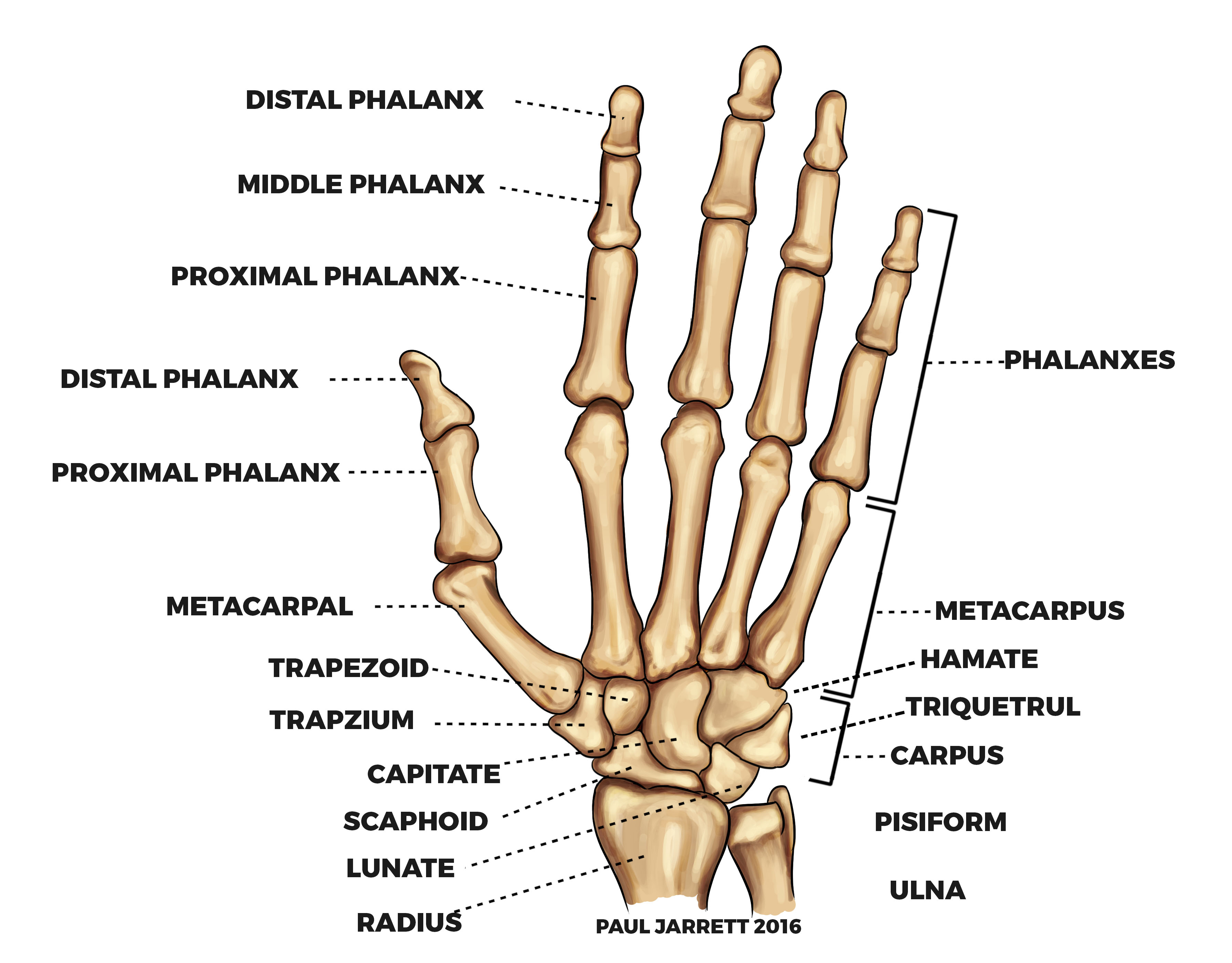
Mr Paul Jarrett Hand and Wrist Anatomy Murdoch Orthopaedic Clinic
Triquetrum. Pisiform. Trapezium. Trapezoid. Capitate. Hamate. Together, these bones connect the lower arm to the hand and fingers as the proximal carpal bones articulate with the radius and ulna to form the wrist joint. These bones articulate with each other, allowing wrist movement so we can perform common daily activities with our hands.
Anatomy of hand skeleton and definition of the palm, fingers (red
Actions: Abducts the thumb. Innervation: Median nerve (recurrent branch). Flexor Pollicis Brevis The flexor pollicis brevis forms the medial aspect of the thenar eminence. It is described as having a superficial and deep part - although the deep component is variable in size.

Intrinsic Hand Muscles MSK Medbullets Step 1
hand, grasping organ at the end of the forelimb of certain vertebrates that exhibits great mobility and flexibility in the digits and in the whole organ. It is made up of the wrist joint, the carpal bones, the metacarpal bones, and the phalanges. The digits include a medial thumb (when viewed with the palm down), containing two phalanges, and.

Anatomy of the Hand Brace Access
Joints. The joints in our hands are made up of cartilage surfaces that cap the bones. Cartilage is a smooth surface that allows for gliding. When cartilage is healthy, there is a cushioning effect of the cartilage that absorbs and evens out the forces across the joint. Our joints typically have a capsule of tough, but flexible, fibrous tissue.
.jpg)
Hand Bone Diagram resource Imageshare
Hand Muscles Anatomy, Functions & Diagram | Body Maps Human body Muscular System Muscles Muscles The hand has several muscles. Some make broad, smooth movements, and others make.
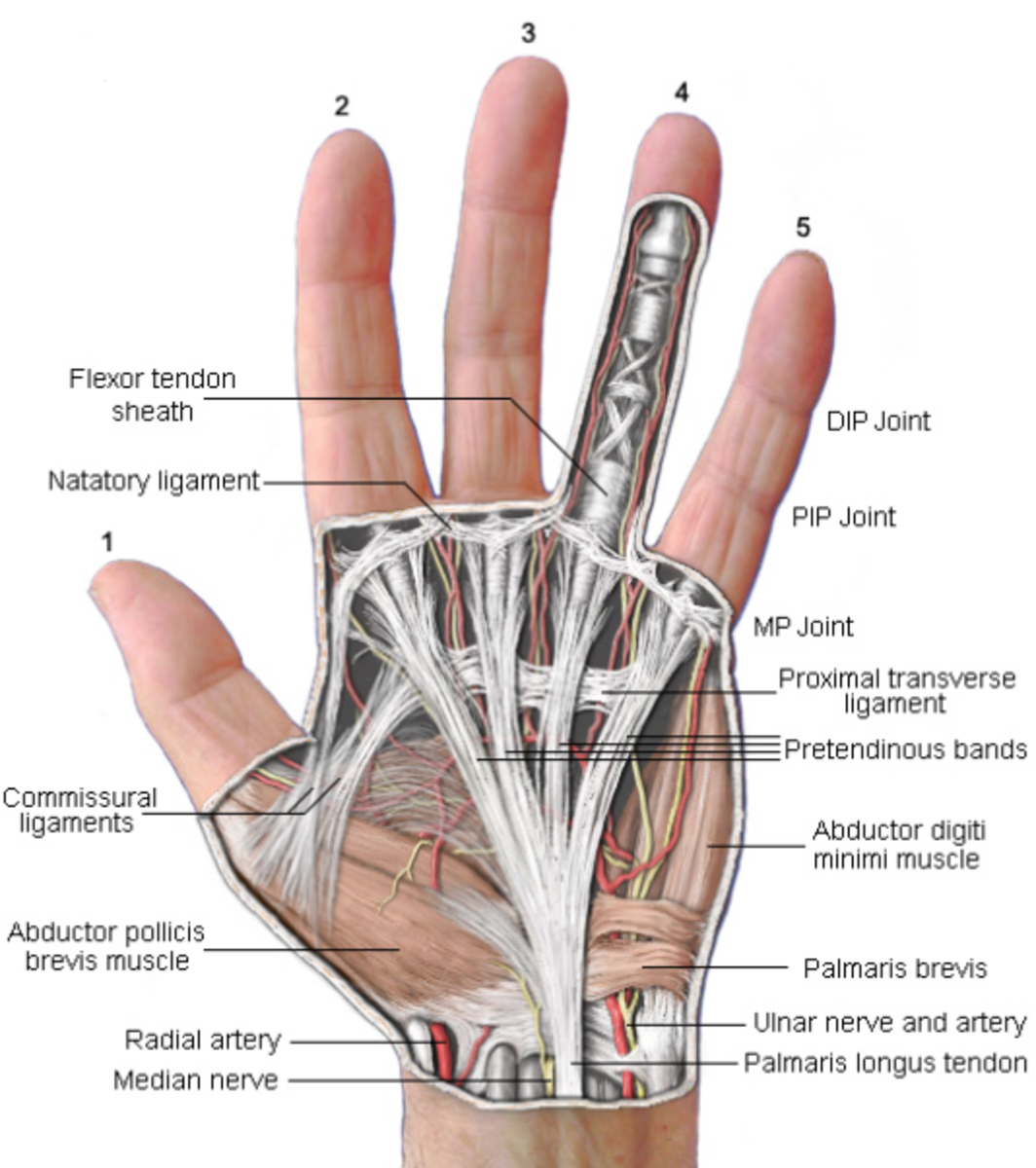
Tendon Injuries of the Hand YouMeMindBody
Basic Hand and Wrist Anatomy. The structure of the human hand is a highly complex. It is composed of skin, blood vessels, nerves, tendons, ligaments, bones and joints. When there is a problem with any of these structures, pain or impaired function may result. Bones and Joints. There are 29 bones in the hand and wrist if you include the radius.

Hand and Wrist Anatomy Murdoch Orthopaedic Clinic
Hand Anatomy, Pictures & Diagram | Body Maps Human body Hand Hand Hands are capable of a wide variety of functions, including gross and fine motor movements. Gross motor movements allow us.